Capped swaps
- Home
- Instruments
- Capped swaps
Fix your price below the market price
Fix your price below the market price in exchange for setting an upper protection limit with a Capped swap
The Capped swap is a combination of a bought swap and a sold call option. It offers the swap buyer a lower level in exchange for limited upside protection.
Here’s an example of how it works. To begin, you and Global agree upon:
- THE MONTHLY VOLUME
- AN OFFICIAL FUEL PRICE INDEX
- A HEDGING PERIOD (E.G. 3 MONTHS)
- THE CAP PRICE
- THE (REDUCED) FIXED PRICE
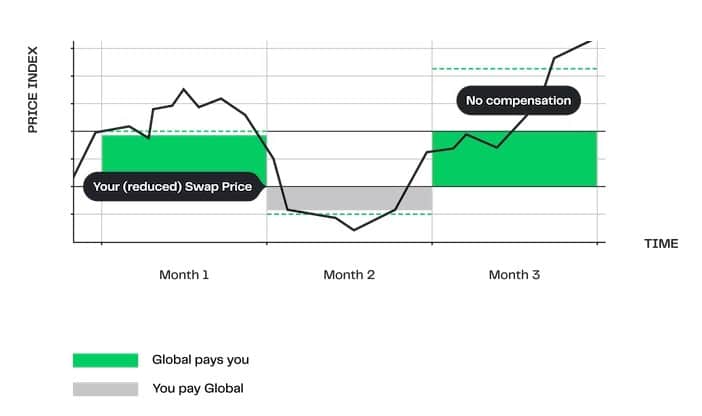
Month 1
Monthly average settles at 115 (20 above the Fixed Price, but below Cap level). Global pays you in full , 20 x volume.
Month 2
Monthly average settles at 90 (5 below the Fixed Price)- You pay Global 5 x volume.
Month 3
Monthly average settles at 130 (35 above the Fixed Price and 10 above the Cap). Global pays you up to Cap level; 25 x
Result
Protection against increasing prices – from a below-market starting point – up to a level where you do not need the protection anymore.
At the end of each calendar month, the settlement amount is based on the difference between the monthly average of the price index and the reduced Fixed Price, up to the point where the Cap level is exceeded.
Three good reasons to use this strategy:
- You do not need full upside protection
- Attractive swap price
- Flexibility in energy supply
BENEFITS
Tailor-made coverage, flexibility in physical supply & reduced swap price
DISADVANTAGES
Limited upside protection & potential basis risk

